I was reading through and tinkering with pieces of information coming my way that related to biocides in general, and herbicide epidemic in India in particular.
Soumik Banerjee, a freelance agro-sociology consultant has been an important source of information from the ground in eastern India. Promotion of sustainable organic agriculture is part of his field of work. He is also one of the rare persons in India that actually bought my book – POISON FOODS OF NORTH AMERICA, and read it through.
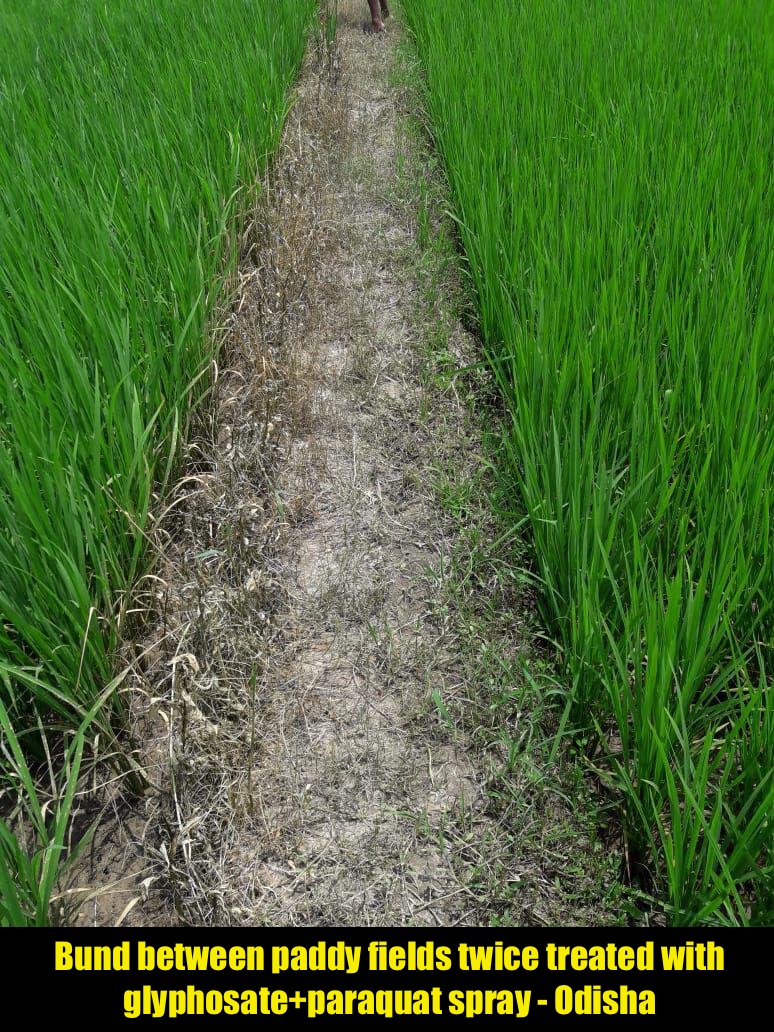 Anyhow, I was playing with some still images and video clips received from him, mostly about the use of glyphosate and other substances such as paraquat in the province of Odisha, India, on the bund around paddy fields. A bund is a raised wall that surrounds small paddy plots. The land is usually made flat so water could stand evenly across the plot. The bund ensures that the water stays and does not flow off. Rice often grows on standing water. This system works in lands with high rainfall and high ground water level during the rainy season in he flood plains. In other words, it suits a monsoon fed India, particularly along the Ganga-Brahmaputra river system of Eastern India.
Anyhow, I was playing with some still images and video clips received from him, mostly about the use of glyphosate and other substances such as paraquat in the province of Odisha, India, on the bund around paddy fields. A bund is a raised wall that surrounds small paddy plots. The land is usually made flat so water could stand evenly across the plot. The bund ensures that the water stays and does not flow off. Rice often grows on standing water. This system works in lands with high rainfall and high ground water level during the rainy season in he flood plains. In other words, it suits a monsoon fed India, particularly along the Ganga-Brahmaputra river system of Eastern India.
Before India adopted modern agro-technology, the land was tilled by domestic cattle – cows or buffalo. They ate the grass that grew on the bund, as well as in the paddy fields off season. The cows left their droppings on the fields. The left over grass, cow dung and other organic matter, rainwater and heat, all did their thing. Worms and micro organisms did mulched and composted the biomass. Nutrients got recycled. Rice was usually grown once only in a year, taking say four months during monsoon. Another crop, a kind of pulse, called Khesari daal, was grown after the rice was harvested. The left over moisture in the soil was enough for this pulse crop. It fixed nitrogen and helped balance the soil nutrient load. Then for the last four months, the land was left to grass, weeds, worms, birds, goats, rats, snakes and nature.
And that was how rice was grown, without any chemical input nor any pumped water, for eons. That was before modernism came into agriculture like an invading army of pillagers. India got agro-modern, agro-civilized and agro-mechanized.
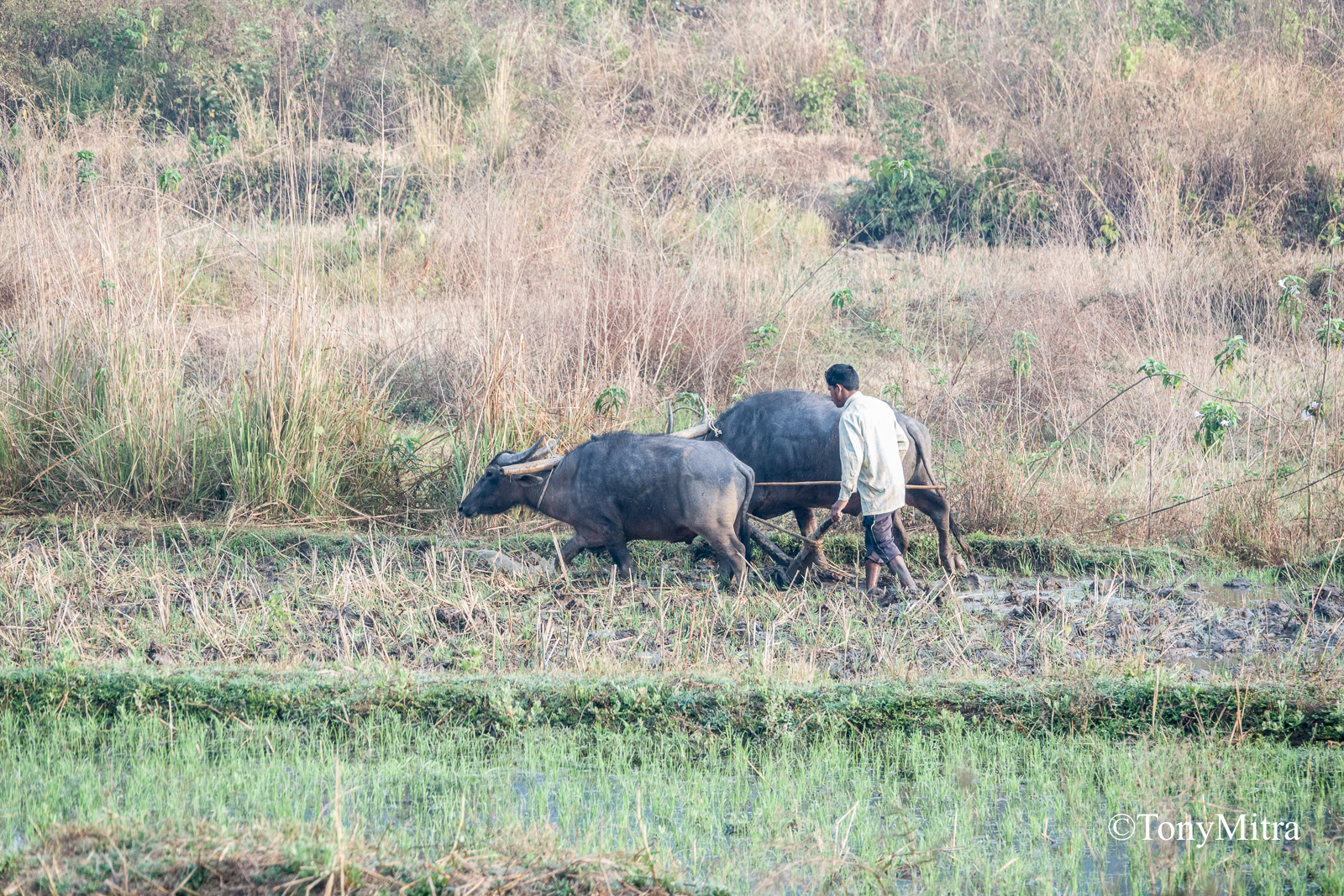 Cattle were ancient and costly to maintain, even if they were ecologically more sustainable than chemicals and fossil fuel dependent machinery. Out went the cows, along with their dung and appetite for grass. In came fossil fuel dependent tractors that spilled industrial lubricants on the soil, left exhaust in the air, and had no use for grass. Since farmers did not usually have money to own such machines, they were rented. Poor farmers had to dole out money to rent these gas guzzlers to till their land.
Cattle were ancient and costly to maintain, even if they were ecologically more sustainable than chemicals and fossil fuel dependent machinery. Out went the cows, along with their dung and appetite for grass. In came fossil fuel dependent tractors that spilled industrial lubricants on the soil, left exhaust in the air, and had no use for grass. Since farmers did not usually have money to own such machines, they were rented. Poor farmers had to dole out money to rent these gas guzzlers to till their land.
That was not all. The idea of crop rotation with Khesari Daal was not good for the GDP of the agro-chemical industry. So, that brand of pulse that was hardy enough to grow without extra work and using the left over moisture of the paddy fields, had to go. So another campaign of misinformation was initiated – Khesari daal, used for generations, was suddenly touted as bad for health. So, the traditional companion of the rice field, Khesari pulse, was banished. In its place came the need for two crops of rice being grown every year out of the same field. People must eat more rice and less varied seeds like pulses.
Also, one needed high yield, this-tolerant, that-intolerant thingamajig kinds of special rice that “unscientific” farmers did not have and could not produce, but scientific institutions could. So these so called hybrid rice was now be used on the field. But these seeds did not come from farmers who would pass successful seeds around for others free of charge. Instead, these magic seeds were the result of hard work of the agro-scientists who worked for firms that were in agriculture business to create a stable market for its products and to make a profit. So the seeds had to be bought.
And since these seeds were hybrid and not stable, nor designed to be stable, they could not be saved by farmers for continuous use. They had to be bought afresh every year. Why make a product that needs to be purchased only once, if you can make the customer buy it again and again and again ?
And since the off season rice did not have the benefit of the monsoon, and since the hybrid rice did not grow out of love and fresh air, but had an unbelievable thirst for water – there were needs for drilling millions of tube wells to pull the water out of the ground. All this activity was financed by bank loans which on paper looked like hectic economic activity and a sign of progress. GDP was rising, India was going to be feeding itself with great food. All was great. Or so the slogan went.
 And with the absence of crop rotation, and disappearance of Khesari pulse, the soil of course would not support two successive crops of rice without nutrient supplement. Smart scientists figured out that plants got carbon, hydrogen and oxygen from air and water. The next three nutrients, nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium, gets depleted by the crop. If most of the leftover stuff is lot allowed to recycle into the soil then the soil needs to be replenished. Thus, the term NPK as combination fertilizer that was to be industrially produced, became a catch word of modern agriculture. This also boosted on paper economic activity, since industry had to cater to this new kind of chemical fertilizer that was not used before.
And with the absence of crop rotation, and disappearance of Khesari pulse, the soil of course would not support two successive crops of rice without nutrient supplement. Smart scientists figured out that plants got carbon, hydrogen and oxygen from air and water. The next three nutrients, nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium, gets depleted by the crop. If most of the leftover stuff is lot allowed to recycle into the soil then the soil needs to be replenished. Thus, the term NPK as combination fertilizer that was to be industrially produced, became a catch word of modern agriculture. This also boosted on paper economic activity, since industry had to cater to this new kind of chemical fertilizer that was not used before.
Somewhere along with it came the need for poisons to kill of pests that usually attacked these hybrid crops that were not naturally hardy to withstand pest attack like the original folk rice varieties did. So, the land had to be inundated with herbicide, pesticide, fungicide, insecticide, etc. All these poisons, grouped together as biocides, are poisons that kill. And if one herbicide did not do the job, why not use two?
Nobody actually did any work on testing if these killer chemicals had any adverse effect on the biomass, on the ecology, and on people.
In came chemical agents. They informed the farmers that the grass on the paddy field as well as on the bund were nasty stuff. Since the cows were not around any more to eat them, they needed to be destroyed, because they host all sorts of dangerous pests. And then they sold glyphosate, along with some more of the toxins that were available. These were not called poison. They were called medicine. They were called vitamin for the soil.
If glyphosate alone was not doing all the job, then another item was added to it – such as paraquat.
Soumik sent me a number of pictures, such as this one from Odisha, where the partition wall between two adjacent fields of paddy, called bund, was twice sprayed by glyphosate and paraquat, to kill all vegetation. That concoction flows into the paddy fields because of the rain, and the water collects and stands in the paddy fields. What this is doing to the soil biology – is not investigated nor told to the farmers. This is how “soil medicine” gets into our food web.
Meanwhile, I was conversing with some US scientists and asking about a questionnaire for the women who gave birth to deformed babies. This was to build up statistics on possible exposure of pregnant women to toxins that might have resulted in the stated birth defects.
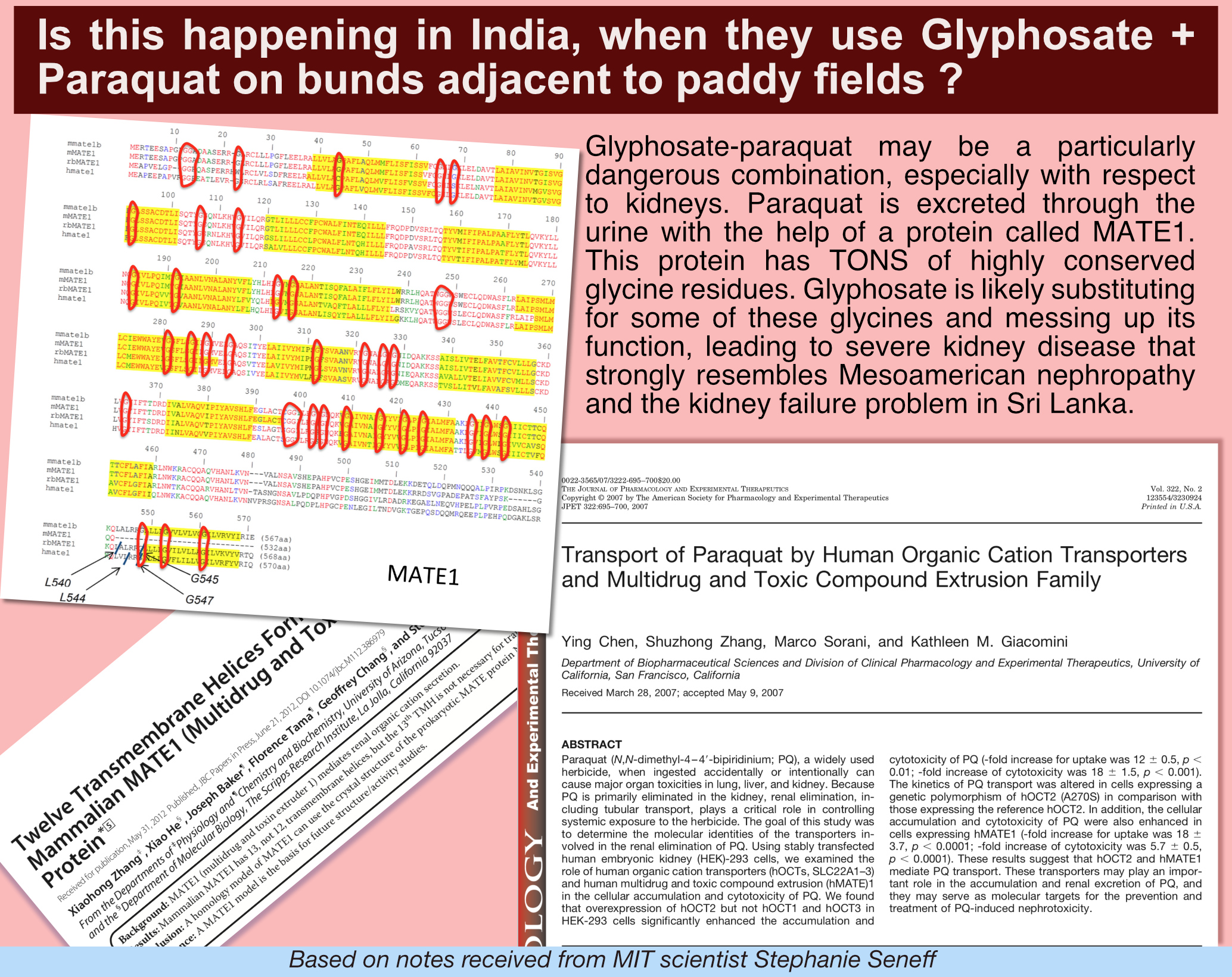
Stephanie Seneff of MIT believed there is cause to believe synergistic damage done to kidneys of farm workers exposed to the glyphosate-paraquat concoction.
Apparently, the human protein called MATE1 is responsible for detoxification of items such as the nasty poison paraquat, most of which might normally be captured by MATE1 that works with our kidneys and allowed to be expelled from the body through urine.
But, we already know that all proteins are constructed from the basic building blocks of 20 amino acids, and the most used of those twenty are glycine. We also know that glyphosate is a biological mimic of glycine and our body does not know how to distinguish one from the other. Therefore when new proteins are being constructed, which is all the time for adults, and at a furious pace for growing children, glyphosate gets to be disincorporated into proteins, if it (glyphosate) is present in our food.
As Dr. Seneff pointed out to me through an email, MATE1 has “tons” of glycine in key positions of that protein, making it very susceptible to being subverted by glyphosate substituting itself in place of some of some glycine in key positions of that protein, thereby rendering MATE1 useless in detoxification work. This, apart from allowing a person being seriously harmed by paraquat itself, also has the ability to permanently damage the kidney – leading to kidney failure that may be linked to the Sri Lanka farm workers as well as the Mesoamerican nephropathy.
 This disease, Mesoamerican nephropathy, was earlier called kidney disease of unknown cause (CKDu), first noticed among young, agricultural workers primarily in Central American nations such as El Salvador, Nicaragua, Guatemala, and Costa Rica.
This disease, Mesoamerican nephropathy, was earlier called kidney disease of unknown cause (CKDu), first noticed among young, agricultural workers primarily in Central American nations such as El Salvador, Nicaragua, Guatemala, and Costa Rica.
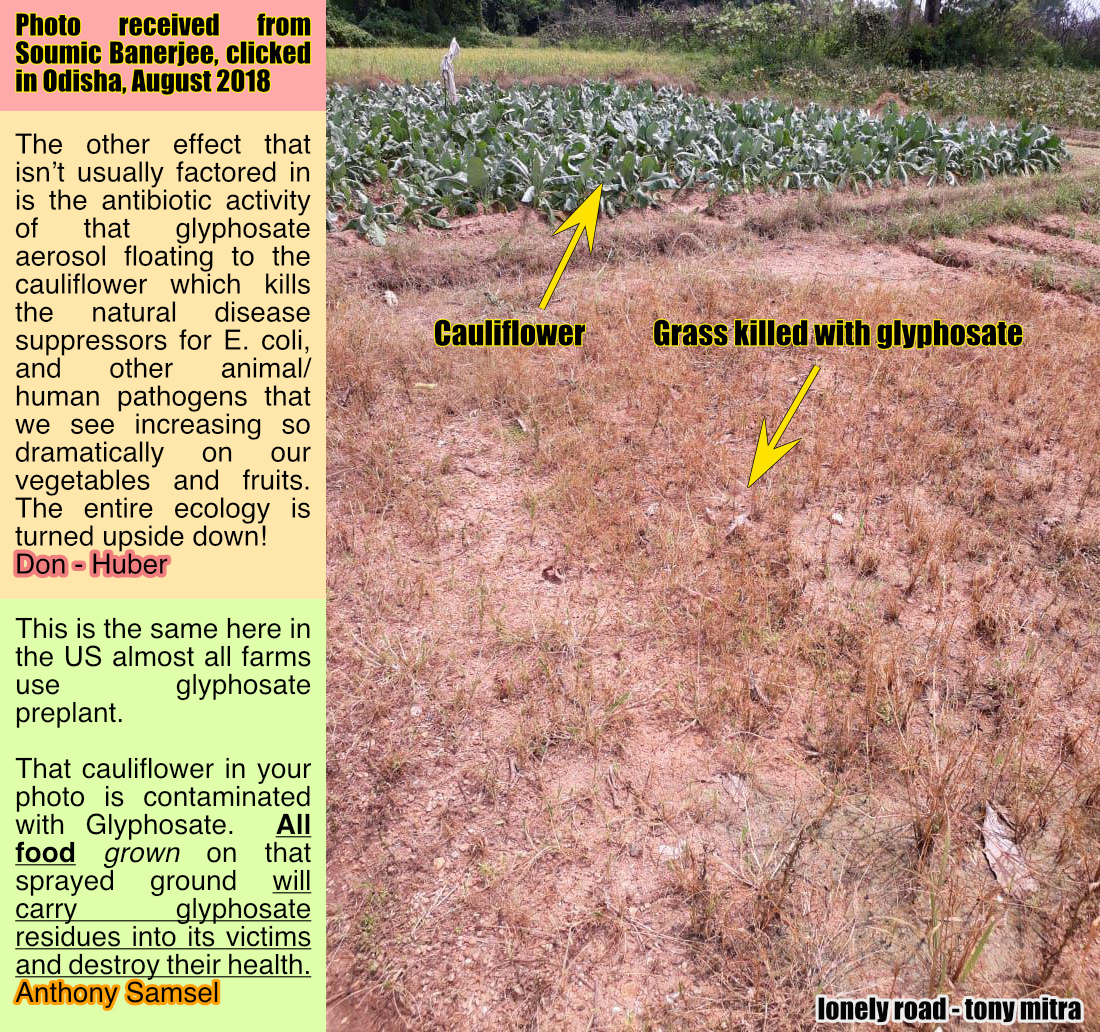
Then there was this other picture, also received from Soumik Bannerjee. It shows a cauliflower patch with brown grass around it, killed by glyphosate. This, when shown to a few scientists, generated instant and spirited response. Comments from Anthony Samsel and Don Huber was included with the picture. There were so many things wrong with this picture. The glyphosate would drift onto the vegetable patch and be picked up by the roots of the Cauliflower. Testing of the vegetable should show presence of glyphosate in it which would poison everything and everyone that eats it. In other words, the cauliflower is sick.
Then there is the issue of aerosol particles of glyphosate drifting and falling on the cauliflower. Its antibiotic activity kicks and inhibits the natural disease suppressors for E. coli and other animal/human pathogens. This phenomenon, when our vegetable begin to make us sick, is an unwanted development that is rising in epidemic proportions across India and elsewhere. As Don aptly said – the entire ecology is turned upside down, all because a handful of dishonest business people manage to hoodwink the entire world, and because folks in India refuse to test, investigate and find out for themselves the truth, and would rather depend on the same entities that sell the poison, to educate us on food nutrition.
 India is not known to keep detailed statistics of health conditions of its citizens, particularly the rural low income class. However, India is supposed to be developing. It is among the fastest rising large emerging nations.
India is not known to keep detailed statistics of health conditions of its citizens, particularly the rural low income class. However, India is supposed to be developing. It is among the fastest rising large emerging nations.
It is time, that India sheds its colonial trappings of the past and begins to take interest in its own affairs. It is time for India to investigate effect of its modern agriculture on the flora, fauna, nature, food, ecology and health of its inhabitants.
It does not take rocket science to allow funding to hospitals and research facilities to start collecting data on one hand, and also testing the effect of these chemicals, single and in synergy, on lab animals, and release the findings for the public.
Glyphosate has not been approved for use in agriculture in India. And yet, it is ubiquitous. It is everywhere in the farm sector. It is not even being called a poison. It is termed as “medicine”. There is a massive campaign of misinformation being conducted by corrupt people with vested interest in pushing these chemicals illegally in agriculture.
The Government and its regulatory authority is apparently not able to keep track of the runaway use of these substances. A few provinces, as it happens appear to be waking up to this menace and contemplating withdrawing license to store or sell glyphosate in areas where there are no tea gardens. The issue is also related to illegal planting of smuggled seeds of GM herbicide tolerant cotton.
There seem to be small signs that some sections of the population is waking up to the danger posed by agro-toxins in general and glyphosate in particular, especially after I came to India and was invited to speak about it in a few towns, an exercise that was supported by a few well meaning NGO and groups.
The task at hand to both record the facts, analyze the statistics, investigate the effects and correct the situation is humongous. But, like all endeavours, it starts with a first few tentative steps.
This article is to be part of my running journal – “Lonely Road”. It is also likely to be shared and circulated as a pdf file. Lastly, it should be also in my blog tonu.org.
And when I speak with farming communities across various rural regions in Bengal – I am likely to mention this. In fact, I did create a slide just for this.
 I have not had much time proof reading these pages. All that would be done later. So, reader is requested to pardon any strange grammar or spelling that might pop up as odd in these pages.
I have not had much time proof reading these pages. All that would be done later. So, reader is requested to pardon any strange grammar or spelling that might pop up as odd in these pages.
